Protein Structure Levels And Function
The tertiary level of protein structure is essentially responsible for the overall shape of the protein molecule which is reflected in its function. The function of a protein is directly dependent on its threedimensional structure.
Protein Structures Primary Secondary Tertiary Quaternary
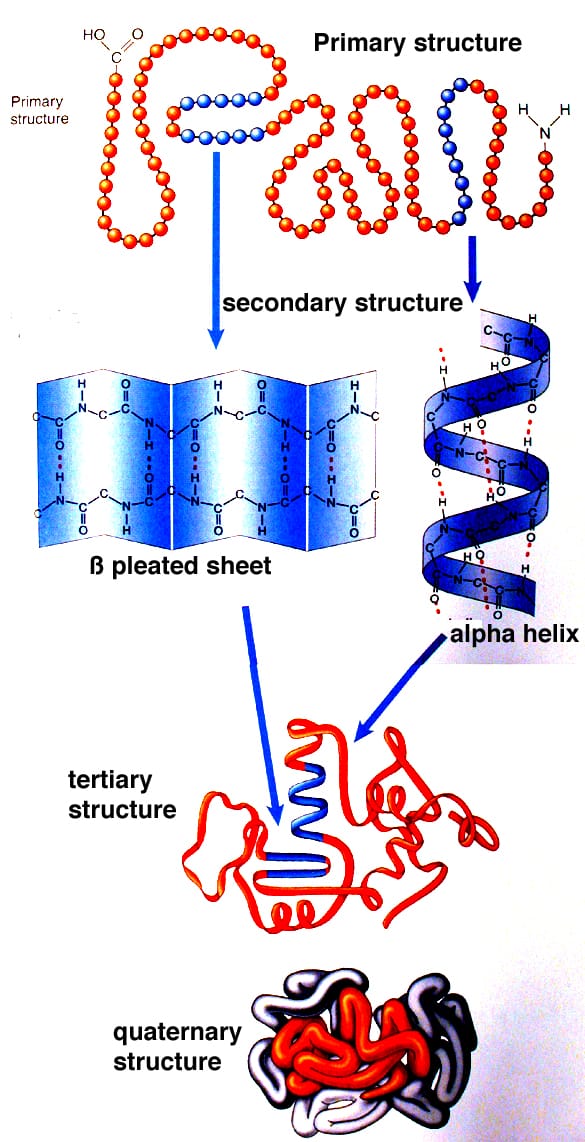
The four levels of protein structure are primary secondary tertiary and quaternary.
Protein structure levels and function. The sequence of a protein is unique to that protein and defines the structure and function of the protein. The simplest level of protein structure primary structure is simply the sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain. It is helpful to understand the nature and function of each level of protein structure in order to fully understand how a protein works.
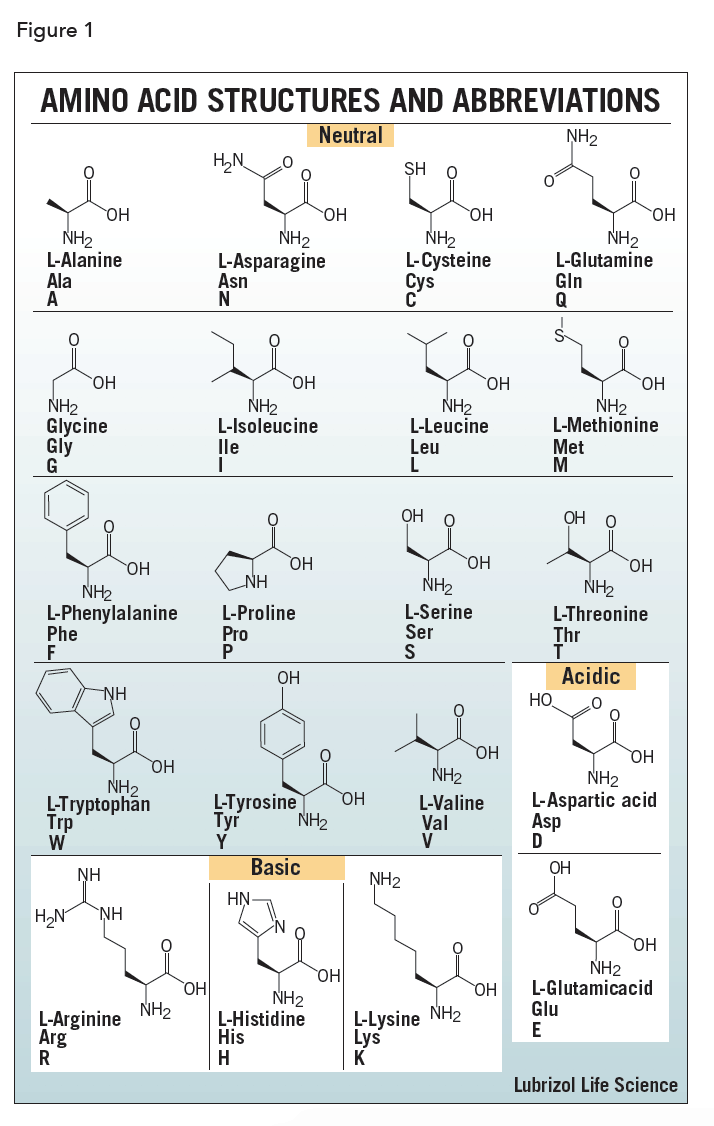
Even with a limited number of amino acid monomers there are only 20 amino acids commonly seen in the human body they can be arranged in a vast number of ways to alter the three dimensional structure and function of the protein. For instance enzymes are mostly globular in shape often with a cleft to expose the active site. For example the hormone insulin has two polypeptide chains a and b shown in diagram below.
Proteins are made up of a long chain of amino acids. The four levels of protein structure are distinguished from one another by the degree of complexity in the polypeptide chain. In total there are seven types of proteins including antibodies enzymes and some types of hormones such as insulin.
A single protein molecule may contain one or more of the protein structure types. Before we dive into prions its necessary to understand the structure of a protein and how it relates to its function. Each protein within the body has a specific function from cellular support to cell signaling and cellular locomotion.
Primary secondary tertiary and quaternary structure. Remarkably proteins spontaneously fold up into three dimensional structures that are determined by the sequence of amino acids in the protein polymer. Often however it is read directly from the sequence of the gene using the genetic code.
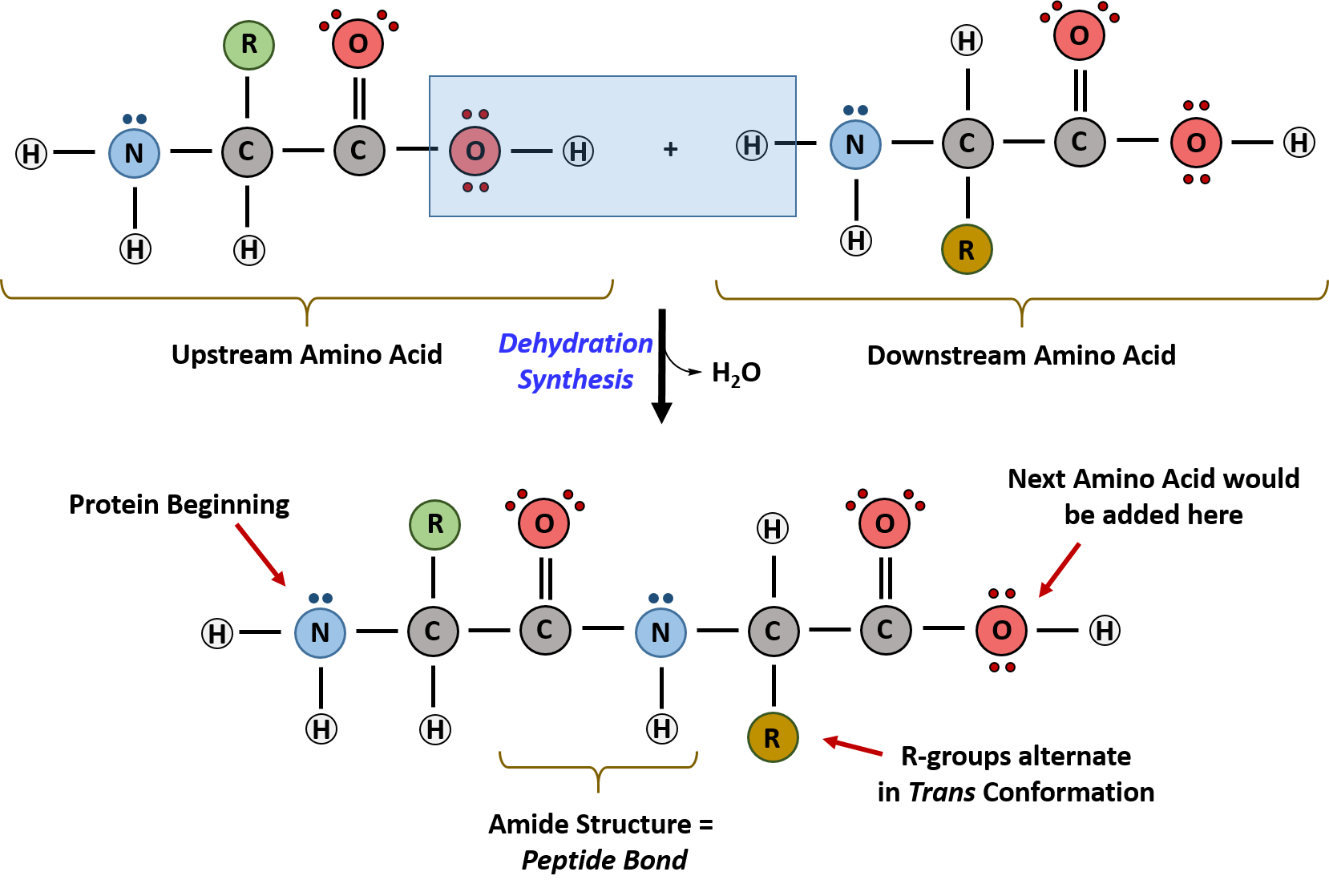
The structure formed when two or more polypeptide chains join together sometimes with an inorganic component to form a protein. Haemoglobin and collagen haemoglobin is a water soluble globular protein which is composed of two α polypeptide chains two β polypeptide chains and an inorganic prosthetic haem group. The sequence of a protein can be determined by methods such as edman degradation or tandem mass spectrometry.
Proteins actually have 4 levels of structure. Proteins are made from strings of amino acids and these chains also known as polypeptides form their primary structure.
Chapter 2 Protein Structure Chemistry
3bheagugapmidm

Biology The Unity And Diversity Of Life 15th Edition
What Are The 4 Structural Levels Of Proteins Quora
What Are The Levels Of A Protein Structure Quora
The Three Dimensional Structure Of Proteins Protein Structure

Structural Biochemistry Proteins Wikibooks Open Books For An
What Are The 4 Structural Levels Of Proteins Quora

Tertiary Structure An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
