Protein Structure And Function
The distinct instructions for the order of amino acids are designated by the genes in a cell. Primary structure is the amino acid sequence.

Membrane Protein Structure Function And Dynamics A Perspective
Proteins properties structure classification and functions proteins are the most abundant biological macromolecules occurring in all cells.
Protein structure and function. They store amino acids function as antibodies act as hormones have structural functions transport important molecules and last but certainly not least proteins can act as enzymes. Proteins are very important molecules that are essential for all living organisms. Protein structure depends on its amino acid sequence and local low energy chemical bonds between atoms in both the polypeptide backbone and in amino acid side chains.
When a cell perceives a need for protein synthesis the dna unravels and is transcribed into an rna copy of the genetic code. Thousands of different kinds ranging in size from relatively small peptides to large polymers. Proteins are involved in virtually all cell functions and a different type of protein is devoted to each role with tasks ranging from general cellular support to cell signaling and locomotion.
Proteins are made up of hundreds or thousands of smaller units called amino acids. The next level of protein structure secondary structure refers to local folded structures that form within a polypeptide due to interactions between atoms of the backbone. It is also the most versatile organic molecule of the living systems and occur in great variety.
Proteins have a wide array of crucial functions in our bodies. The order of amino acids establishes a proteins structure and specific function. Rigid units can function as structural elements in the cytoskeleton the internal scaffolding within cells or in connective tissue.
Parts of proteins with limited flexibility may act as hinges springs. By dry weight proteins are the largest unit of cells. Proteins are made up of a long chain of amino acids.
When you hear the word protein the first you may think about is a bodybuilder or a fancy protein shake but theres so much more to pete than bodybuilding and shakes. Meet pete the protein. If a protein loses its shape at any structural level it may no longer be functional.
Some proteins are quite rigid whereas others display limited flexibility. The backbone just refers to the polypeptide chain apart from the r groups so all we mean here is that secondary structure does not involve r group atoms. Protein structure plays a key role in its function.
Proteins are large complex molecules that play many critical roles in the body. They do most of the work in cells and are required for the structure function and regulation of the bodys tissues and organs. Even with a limited number of amino acid monomers there are only 20 amino acids commonly seen in the human body they can be arranged in a vast number of ways to alter the three dimensional structure and function of the protein.

Bcr Abl Cancer Protein Structure And Function Interactive For 9th
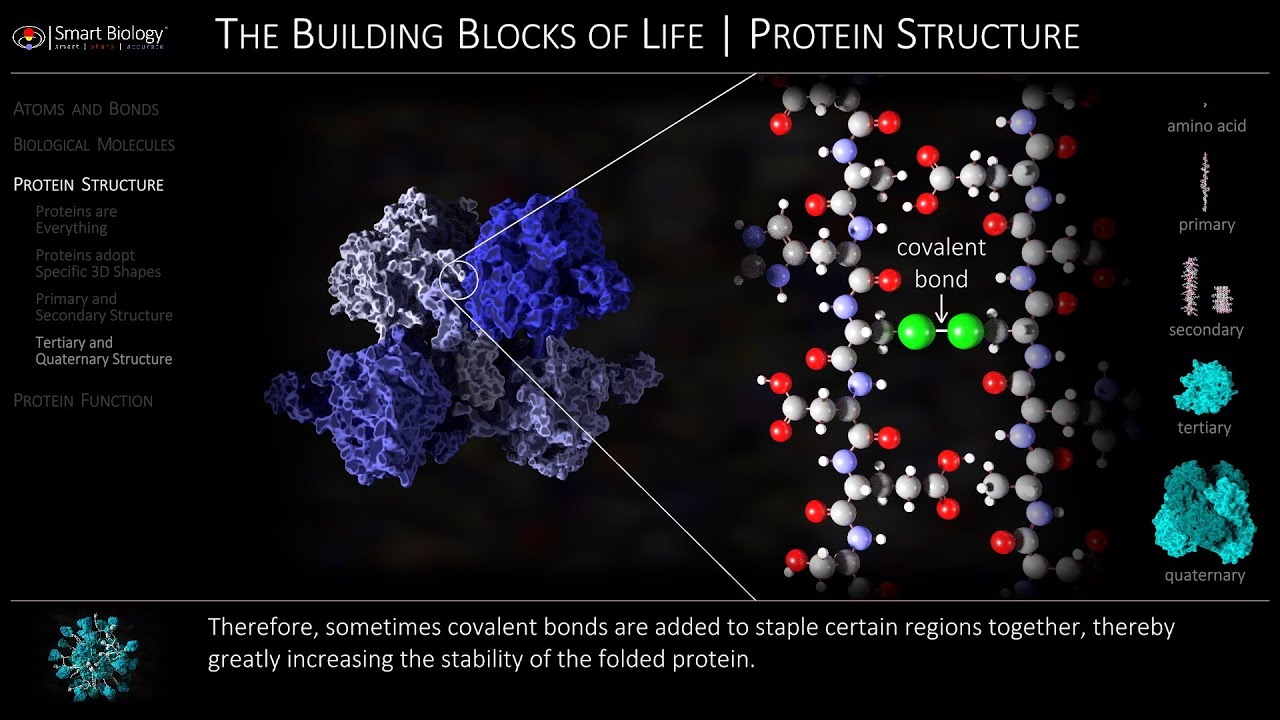
Protein Structure And Function Youtube
The Basics Of Protein Structure And Function Interactive Biology

Work Flow For Acid Stable Protein Structure And Function
Http Genome Tugraz At Molecularbiology Ws11 Chapter03 Pdf
Tertiary Structure Protein Structure Tutorials Msoe Center For
Protein Molecular Structure

Membrane Protein Structure And Function Characterization Methods
Proteins Structure And Functions