Tertiary Protein Structure Diagram
While individual amino acids in the primary sequence can interact with one another to form secondary structures such as helices and sheets and individual amino acids from distant parts of the primary. Tertiary structure is the three dimensional structure of a protein.

Bi Ol O Gy Biˈaləje Protein Structure
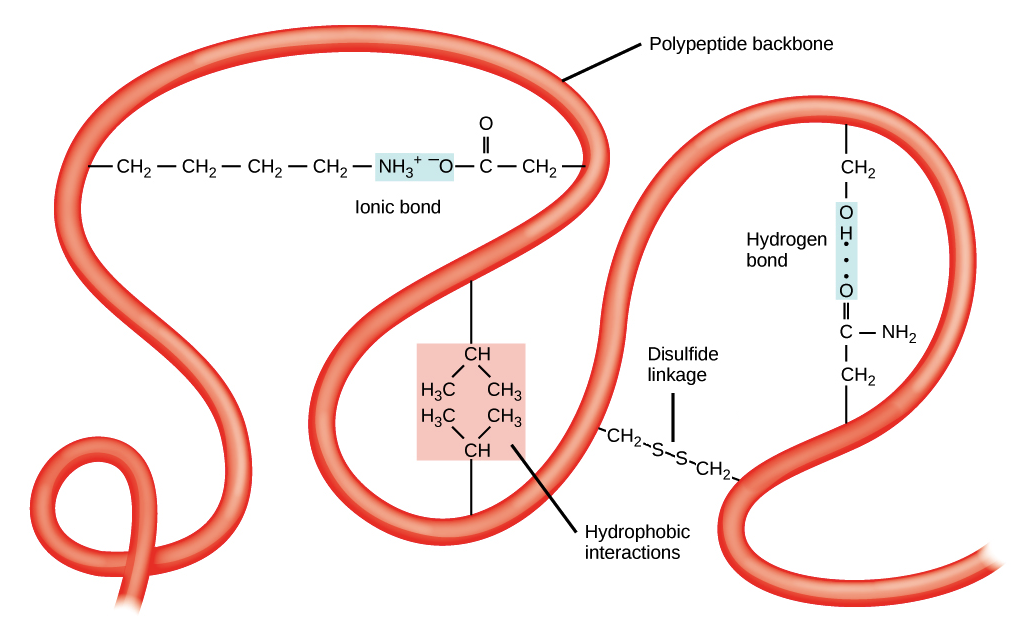
Amino acid side chains may interact and bond in a number of ways.

Tertiary protein structure diagram. The tertiary structure of a protein is a description of the way the whole chain including the secondary structures folds itself into its final 3 dimensional shape. A protein needs to adopt a final and stable 3 dimensional shape in order to function properly. The overall three dimensional structure of a polypeptide is called its tertiary structure.
Primary secondary tertiary and quaternary structure. Knowing the structure of a similar homologous sequence for example a member of the same protein family allows highly accurate prediction of the tertiary structure by homology modeling. It can also refer to biomolecular complexes of proteins with nucleic acids and other cofactors.
Protein tertiary structure is the three dimensional shape of a protein. The tertiary structure of a protein is the arrangement of the secondary structures into this final 3 dimensional shape. The aim of most protein structure databases is to organize and annotate the protein structures providing the biological community access to the experimental data in a useful way.
The tertiary structure will have a single polypeptide chain backbone with one or more protein secondary structures the protein domains. A single protein molecule may contain one or more of the protein structure types. Protein quaternary structure is the number and arrangement of multiple folded protein subunits in a multi subunit complex.
Tertiary structure is the next level of complexity in protein folding. The tertiary structure is primarily due to interactions between the r groups of the amino acids that make up the protein. What is tertiary structure.
If the full length protein sequence is available it is possible to estimate its general biophysical properties such as its isoelectric point. Protein structure database is a database that is modeled around the various experimentally determined protein structures. This is often simplified into models like the following one for the enzyme dihydrofolate reductase.
Tertiary protein structure refers to the manner in which the helical and non helical regions of a polypeptide are folded back on themselves to add yet another order of shape to the molecule. The tertiary structure of proteins. The interactions and bonds of side chains within a particular protein determine its tertiary structure.
In globular proteins it is the non helical regions that permit the folding. The overall 3 dimensional shape of a protein. It includes organisations from simple dimers to large homooligomers and complexes with defined or variable numbers of subunits.
The four levels of protein structure are distinguished from one another by the degree of complexity in the polypeptide chain.

Tertiary Structure An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
G Predicting Secondary And Tertiary

As Biology Proteins Diagram Quizlet
Pearson The Biology Place
4 Levels Of Protein Structure With Diagram
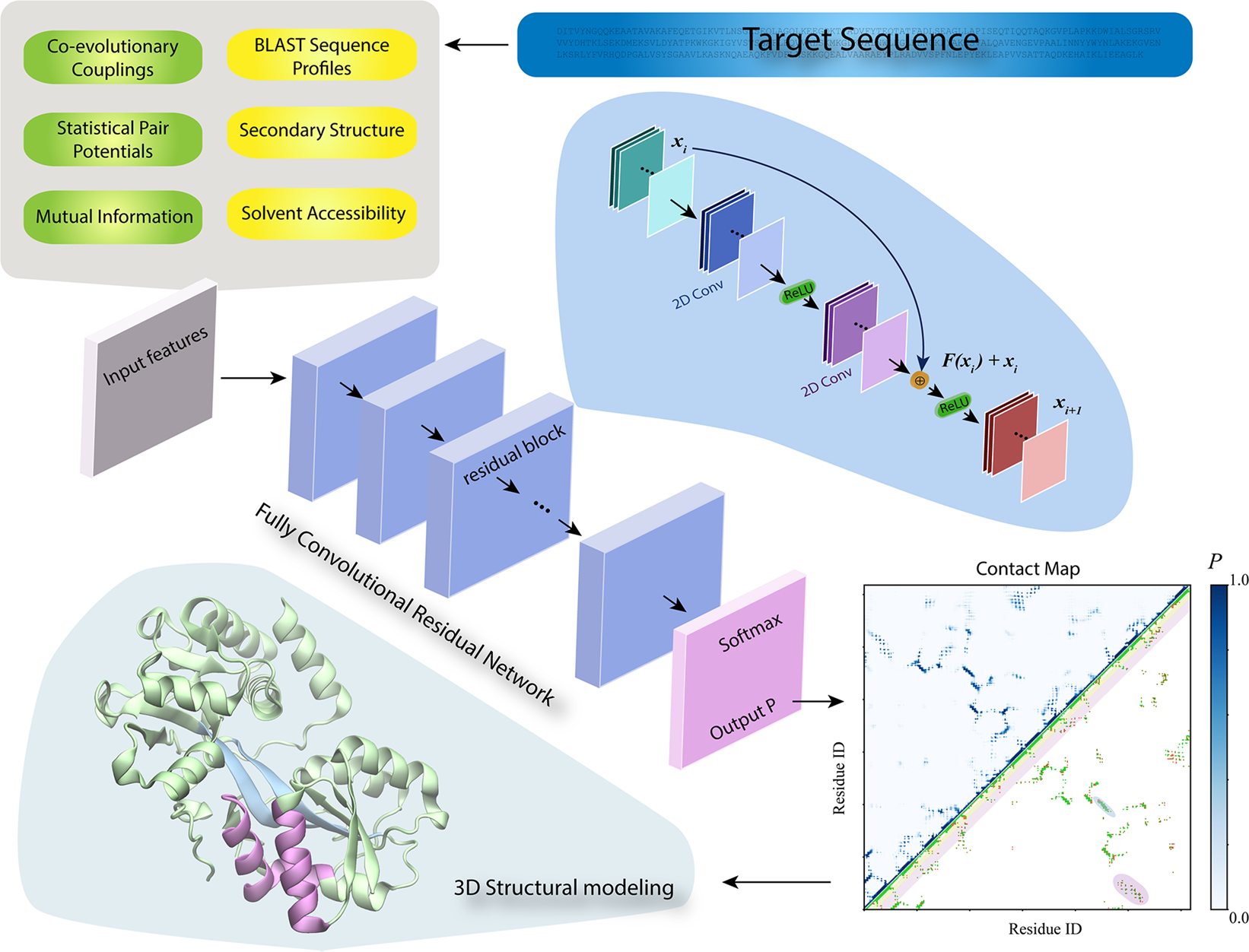
Destini A Deep Learning Approach To Contact Driven Protein

Protein Structure Wikipedia
Protein Structure Primary Secondary Tertiary Quatrenary

Protein Structure Learn Science At Scitable