Simple Protein Structure Diagram
Protein structures range in size from tens to several thousand amino acids. They are polymers formed from 20 possible amino acids by rna translation.
The Anatomy And Taxonomy Of Protein Structures
If you just want the bare minimum of the protein structure you can just show the backbone right like in 1c and 2c in our gallery of images above.

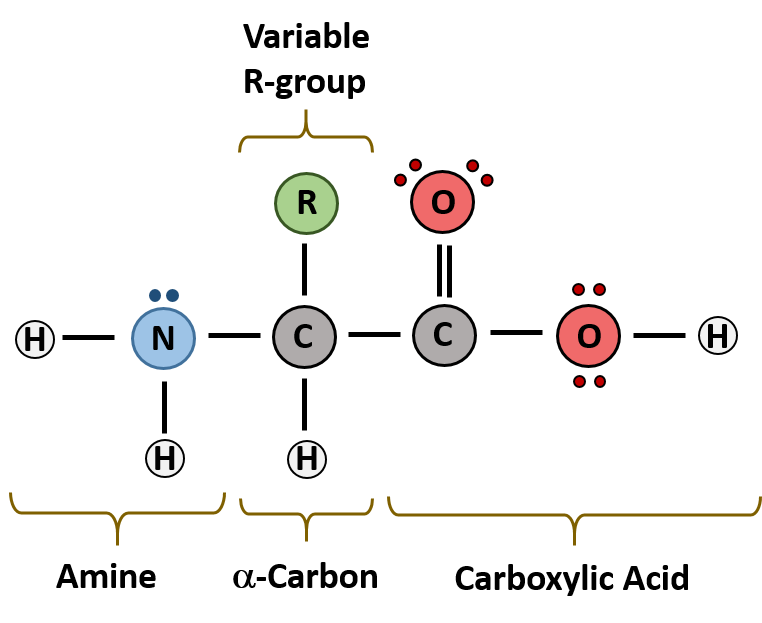
Simple protein structure diagram. Four protein structure types. Amino acids all have the general structure. For example the hormone insulin has two polypeptide chains a and b shown in diagram below.
Then the amino acids that are created in the cell are linked together in a certain order. The basic structure of an a amino acid is quite simple. This type of model ignores the structure of the individual amino acids and just shows the backbone of the protein where the amino acids are hooked together.
This structure is what makes proteins work. The protein that is created has a specific job to do or a specific tissue such as muscle tissue to create. These interactions play a major role in protein folding and give proteins their 3 d structure.
The simplest level of protein structure primary structure is simply the sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain. We notice that the c a atom has 4 different ligands the h is omitted in the drawing and is thus chiral. The primary structure of a polypeptide chain is delineated beginning with the amino acid occupying the polypeptides n terminus.
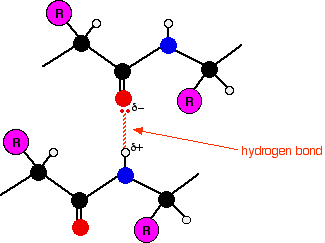
The nonpolar amino acids are hydrophobic. Nonpolar amino acids are the opposite hydrophobic in that they avoid contact with liquid. Polypeptide chain of the protein molecule is held in a coiled or helical shape by hydrogen bonds which are established in between the peptide linkages.
After translation proteins fold into specific shapes. The four levels of protein structure are distinguished from one another by the degree of complexity in the polypeptide chain. The primary structure of a protein is the order of these amino acids in the backbone of each of the polypeptide chains comprising the molecule.
Proteins are important biological macromolecules present in all organisms. The structure of amino acids is fairly simple. A single protein molecule may contain one or more of the protein structure types.
R denotes any one of the 20 possible side chains see table below. To understand how proteins work. Each protein is made up of a unique number and order of amino acids.
The coiled or helical shape of polypeptide chain constitutes the α helix or secondary structure of the protein fig. Below is a listing of the 20 amino acids grouped by their r group properties. This is not done by chemical bonds but by weaker forces such as hydrogen bonds.
Structure of proteins carbohydrates and fats anthony carpi carbohydrates visionlearning vol. R denotes any one of the 20 possible side chains see table below. Protein structure describes how protein molecules are organised.
The simple sugars and those carbohydrates that are made of. Primary secondary tertiary and quaternary structure. The r in the diagram represents a functional group that varies.

Protein Design A Perspective From Simple Tractable Models
Chapter 2 Protein Structure Chemistry
Protein Structure

Tertiary Structure An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
24 4 Protein Metabolism Anatomy And Physiology
/protein-structure-373563_final11-5c81967f46e0fb00012c667d.png)
Four Types Of Protein Structure

Protein Structure Bioninja

Protein Structure Prediction Wikipedia

Chem 153a Study Guide Winter 2019 Quiz John Torrey Torr